| 4.1 | Given: h(x)=x−1−3+2 | |
| 4.1.1 | Write down the equations of the asymptotes of h. | (2) |
| 4.1.2 | Determine the equation of the axis of symmetry of h that has a negative gradient. | (2) |
| 4.1.3 | Sketch the graph of h, showing the asymptotes and the intercepts with the axes. | (4) |
| 4.2 | The graphs of f(x)=21(x+5)2−8 and g(x)=21x+29 are sketched below. - A is the turning point of f.
- The axis of symmetry of f intersects the x-axis at E and the line g at D(m;n).
- C is the y-intercept of f and g.
|
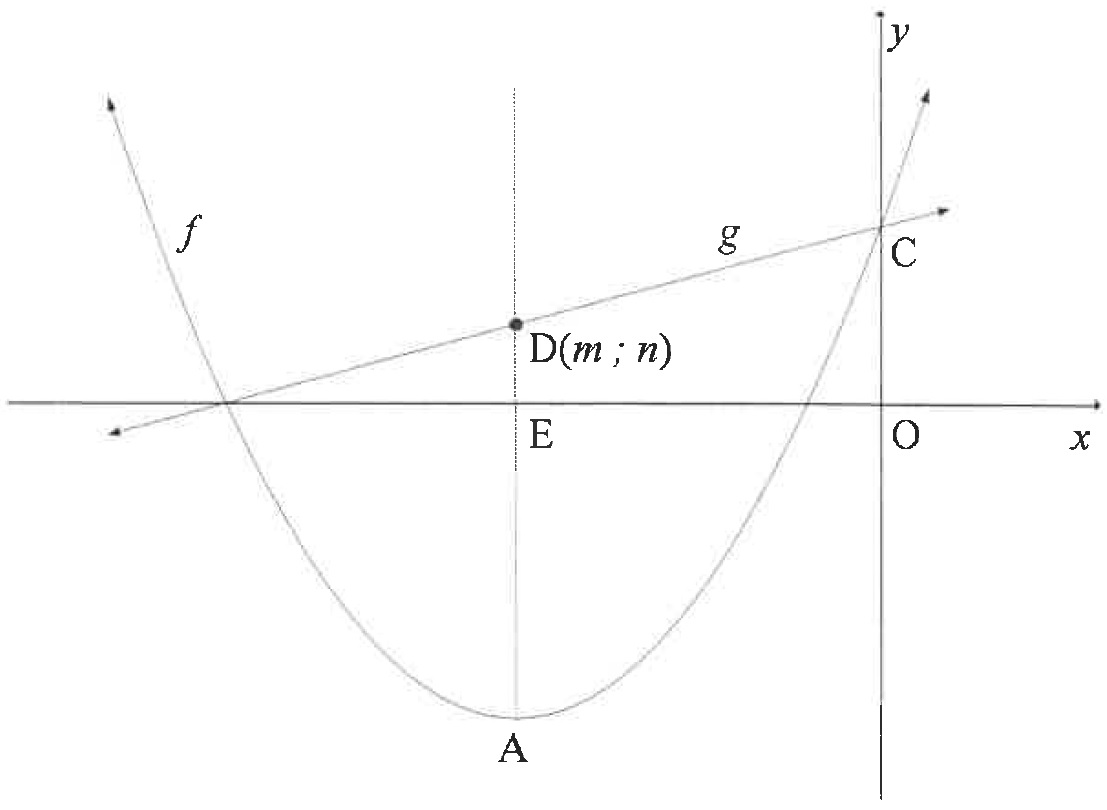 |
| 4.2.1 | Write down the coordinates of A. | (2) |
| 4.2.2 | Write down the range of f. | (1) |
| 4.2.3 | Calculate the values of m and n. | (3) |
| 4.2.4 | Calculate the area of OCDE. | (3) |
| 4.2.5 | Determine the equation of g−1, the inverse of g, in the form y=... | (2) |
| 4.2.6 | If h(x)=g−1(x)+k is a tangent to f, determine the coordinates of the point of contact between h and f. | (4) |
| | [23] |
